| Image | Description | PDF File |
|---|---|---|
 | Louvet-Vallee, S., Kolotuev, I., Podbilewicz, B., and Felix, M.A. (2003). Control of vulval competence and centering in the nematode Oscheius sp. 1 CEW1. Genetics 163, 133-146 | |
 | Shemer, G., and Podbilewicz, B. (2002). LIN-39/Hox triggers cell division and represses EFF-1/fusogen-dependent vulval cell fusion. Genes & development 16, 3136-3141. | |
 | Mohler, W.A., Shemer, G., del Campo, J.J., Valansi, C., Opoku-Serebuoh, E., Scranton, V., Assaf, N., White, J.G., and Podbilewicz, B. (2002). The type I membrane protein EFF-1 is essential for developmental cell fusion. Developmental cell 2, 355-362. | |
 | Rabin, Y., and Podbilewicz, B. (2000). Temperature-controlled microscopy for imaging living cells: apparatus, thermal analysis and temperature dependency of embryonic elongation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Journal of microscopy 199, 214-223. | |
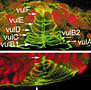 | Shemer, G., Kishore, R., and Podbilewicz, B. (2000). Ring formation drives invagination of the vulva in Caenorhabditis elegans: Ras, cell fusion, and cell migration determine structural fates. Developmental biology 221, 233-248. | |
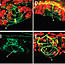 | Sharma-Kishore, R., White, J.G., Southgate, E., and Podbilewicz, B. (1999). Formation of the vulva in Caenorhabditis elegans: a paradigm for organogenesis. Development 126, 691-699. | |
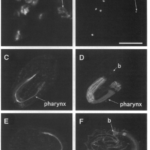 | Podbilewicz, B. (1996). ADM-1, a protein with metalloprotease- and disintegrin-like domains, is expressed in syncytial organs, sperm, and sheath cells of sensory organs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular biology of the cell 7, 1877-1893. | |
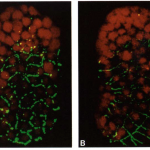 | Podbilewicz, B., and White, J.G. (1994). Cell fusions in the developing epithelial of C. elegans. Developmental biology 161, 408-424. | |
 | Podbilewicz, B., and Mellman, I. (1990). ATP and cytosol requirements for transferrin recycling in intact and disrupted MDCK cells. The EMBO journal 9, 3477-3487. |