| Image | Description | Link/PDF File |
|---|---|---|
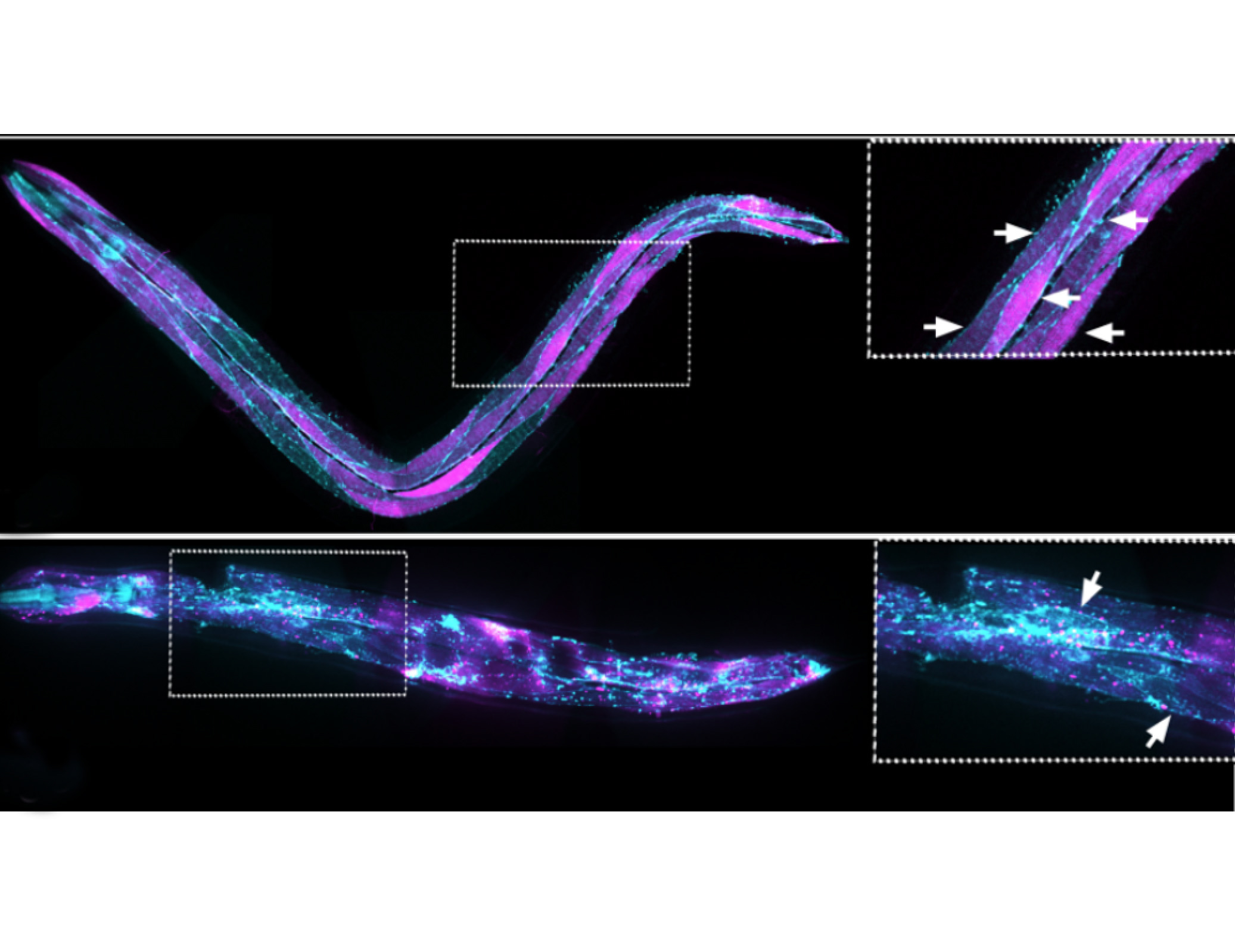
 | Iosilevskii I, Hall DH, Katz M, Podbilewicz P. "The PVD neuron has male-specific structure and mating function in Caenorhabditis elegans". 2025, PNAS 122 (13) e2421376122. | Link |
 | Inberg S, Iosilevskii Y, Calatayud-Sanchez A, Setty H, Oren-Suissa M, Krieg M, Podbilewicz B. (2025). "Sensory experience controls dendritic structure and behavior by distinct pathways involving degenerins". eLife 14:e83973. | Link |
 | Iosilevskii I, Yuval O, Shemesh T, Podbilewicz P. "Protocol for neuron tracing and analysis of dendritic structures from noisy microscopy images using Neuronalyzer". STAR Protocols. 2024 | Link |
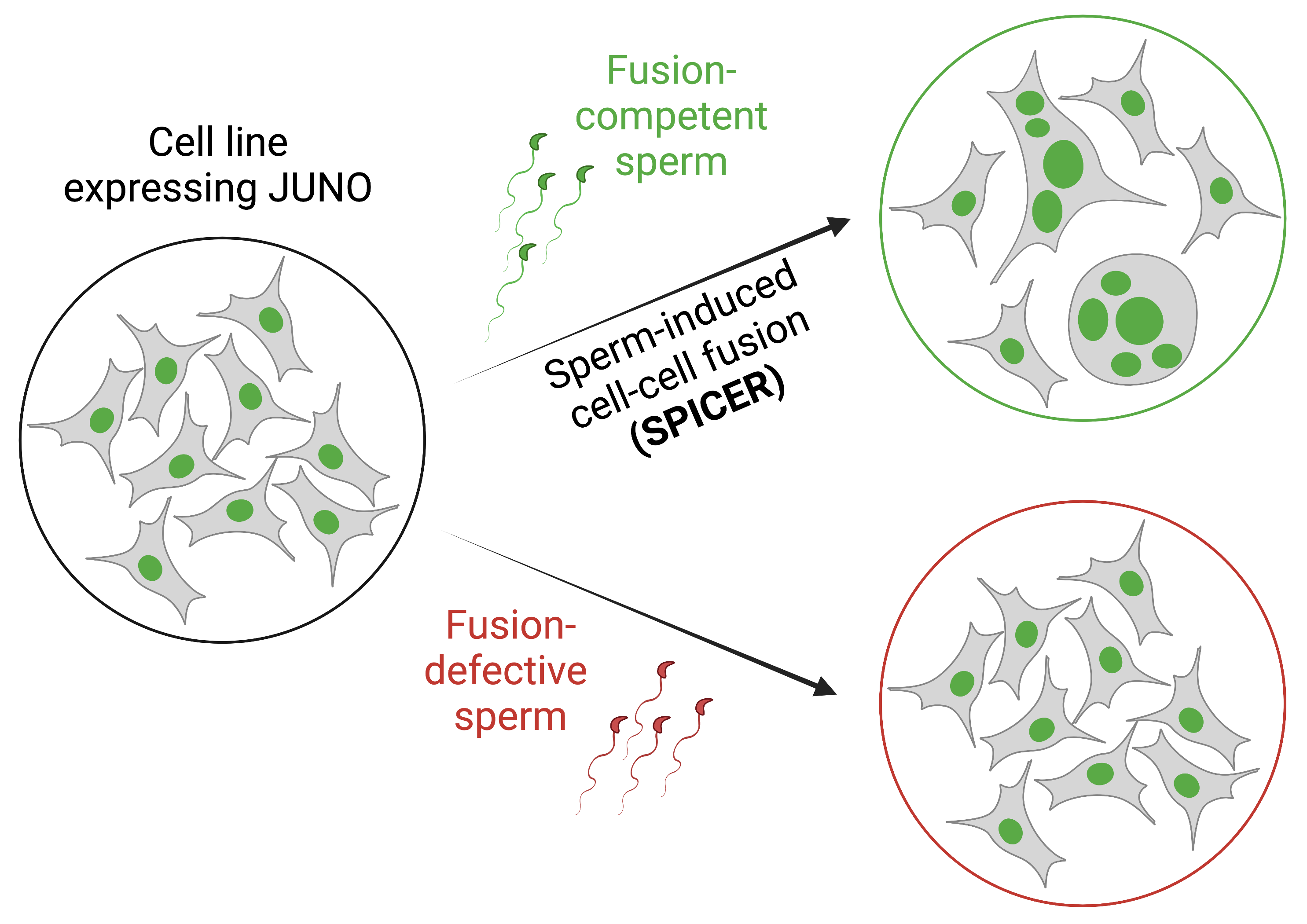 | Brukman NG, Valansi C, Podbilewicz B. "Sperm induction of somatic cell-cell fusion as a novel functional test". Elife. 2024 Jan 24;13. doi: 10.7554/eLife.94228. PubMed PMID: 38265078. | Link |
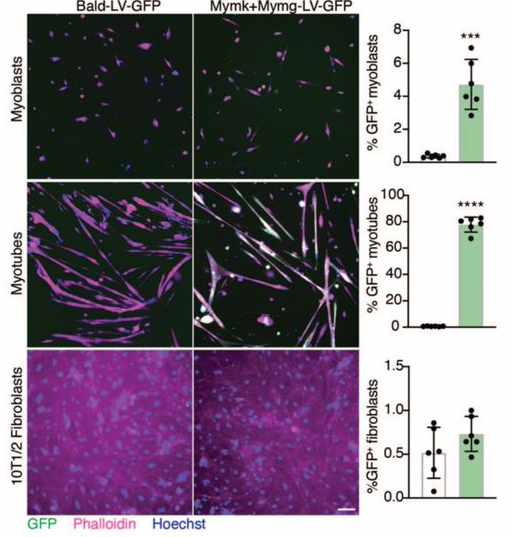 | Hindi SM, Petrany MJ, Greenfeld E, Focke LC, Cramer AAW, Whitt MA, Khairallah RJ, Ward CW, Chamberlain JS, Prasad V, Podbilewicz B, Millay DP. Enveloped viruses pseudotyped with mammalian myogenic cell fusogens target skeletal muscle for gene delivery. Cell. 2023 Aug 3;186(16):3520. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.025. PubMed PMID: 37541201. | Link |
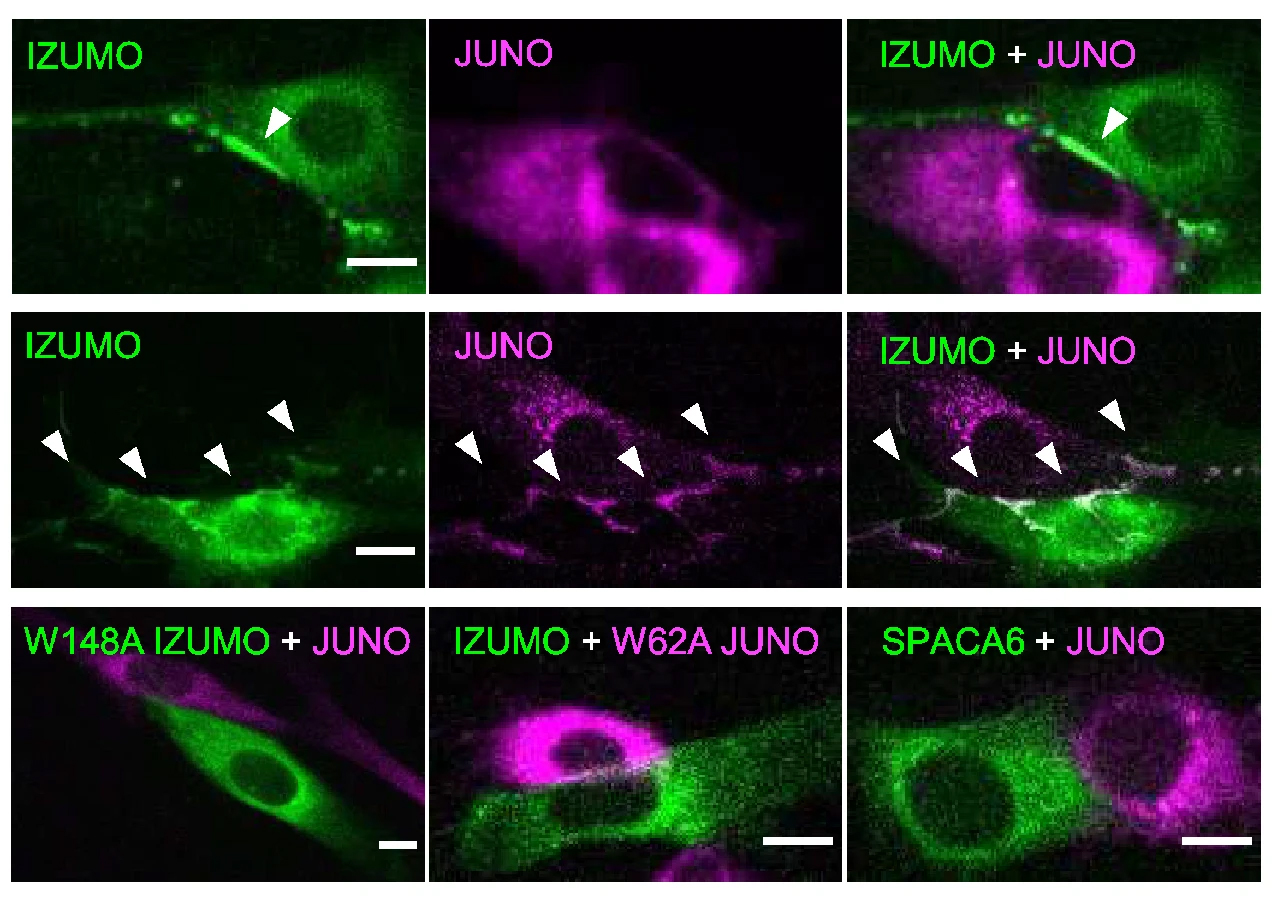
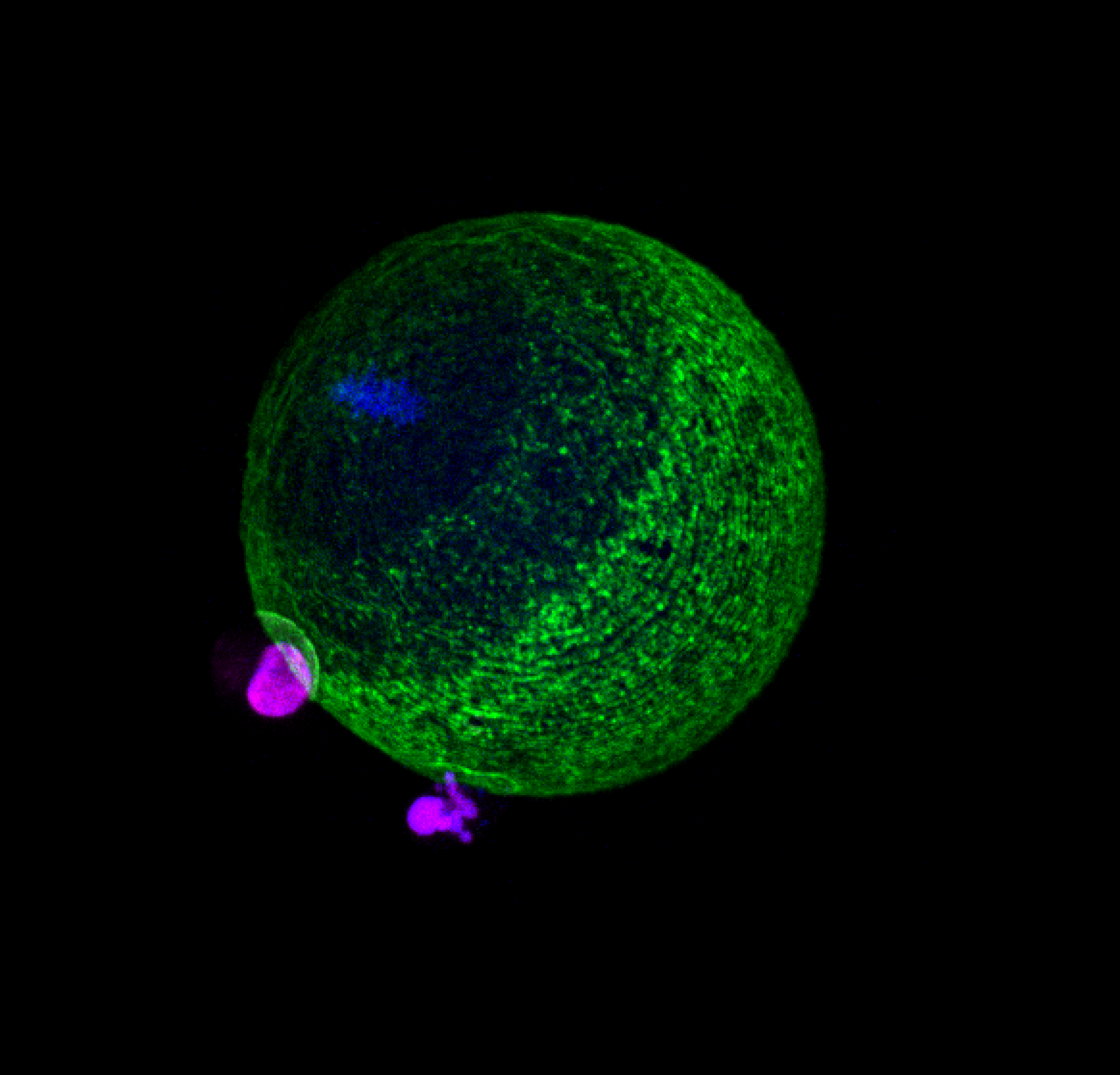 | Brukman N.G., Nakajima K.P., Valansi C., Li X. Higashiyama T., Podbilewicz B. "A novel function for the sperm adhesion protein IZUMO1 in cell–cell fusion" J Cell Biol (2023) 222 (2): e202207147. | Link |
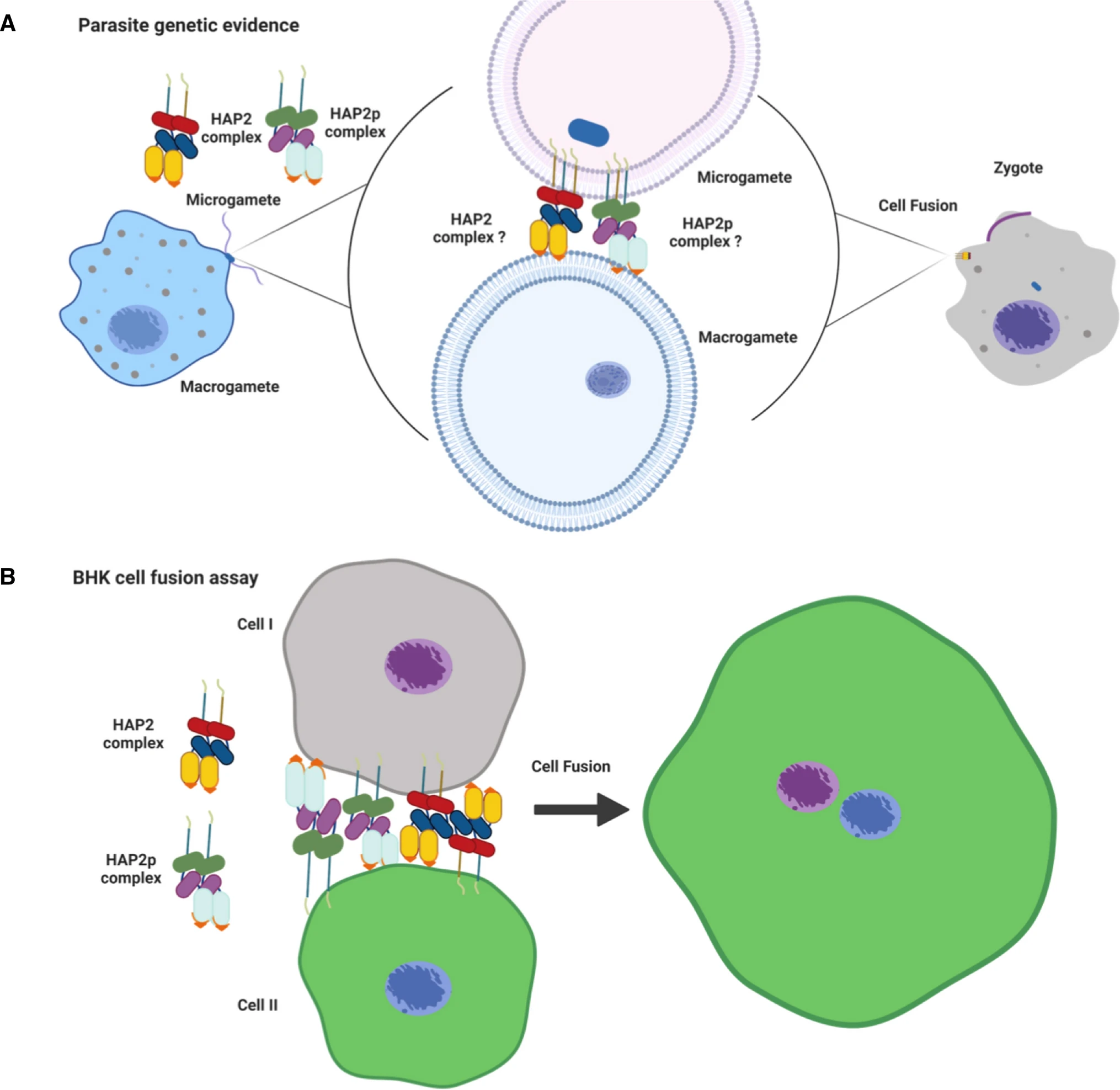 | Kumar S., Valansi C., Haile M.T., Li X., Flyak K., Dwivedy A., Abatiyow B.A., Leeb A.S., Kennedy S.Y., Camargo N.M., Vaughan A.M., Brukman N.G., Podbilewicz B., Kappe SHI. (2022) "Malaria parasites utilize two essential plasma membrane fusogens for gamete fertilization" Cell Mol Life Sci. 79(11):549. | Link |
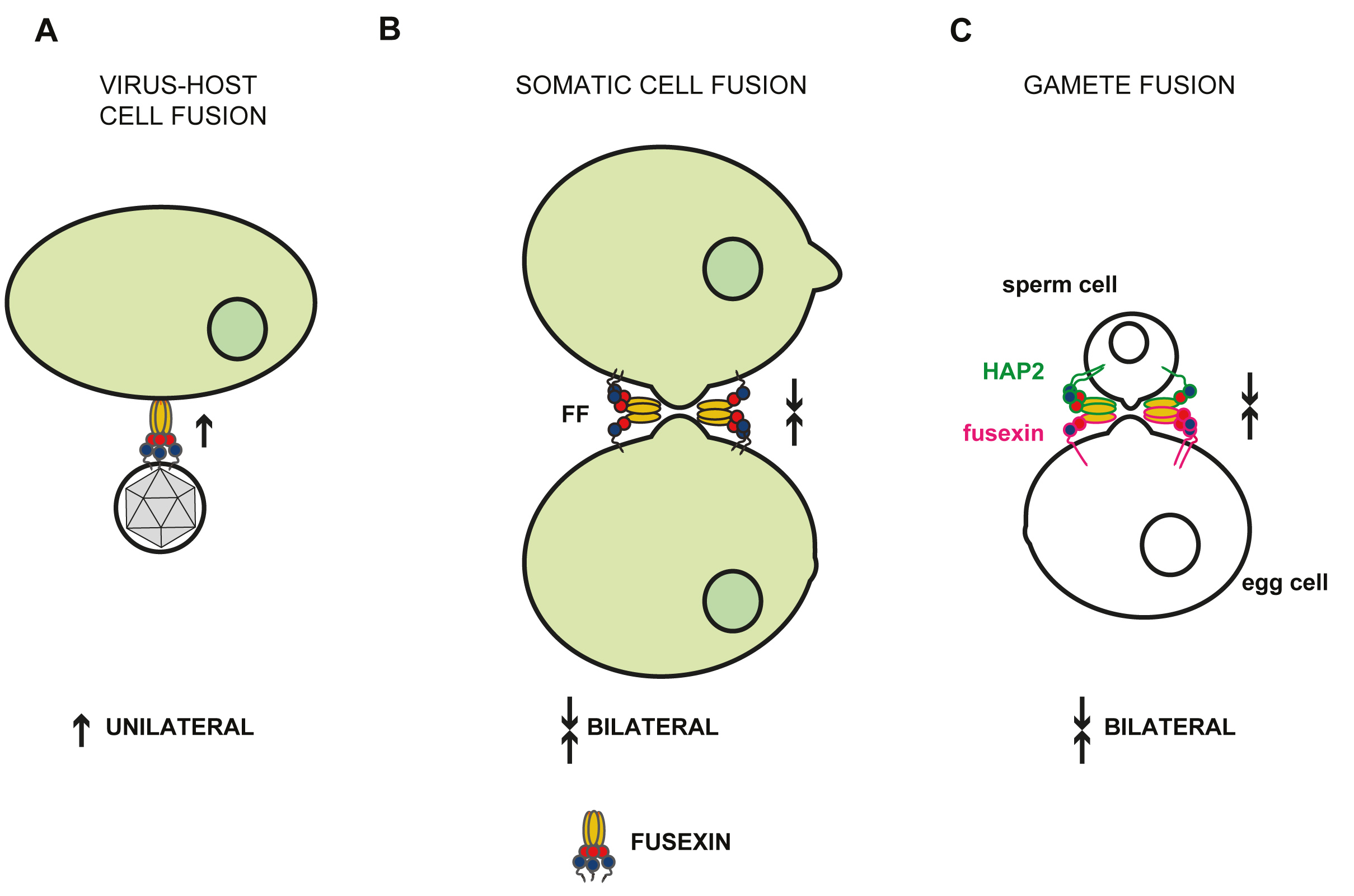
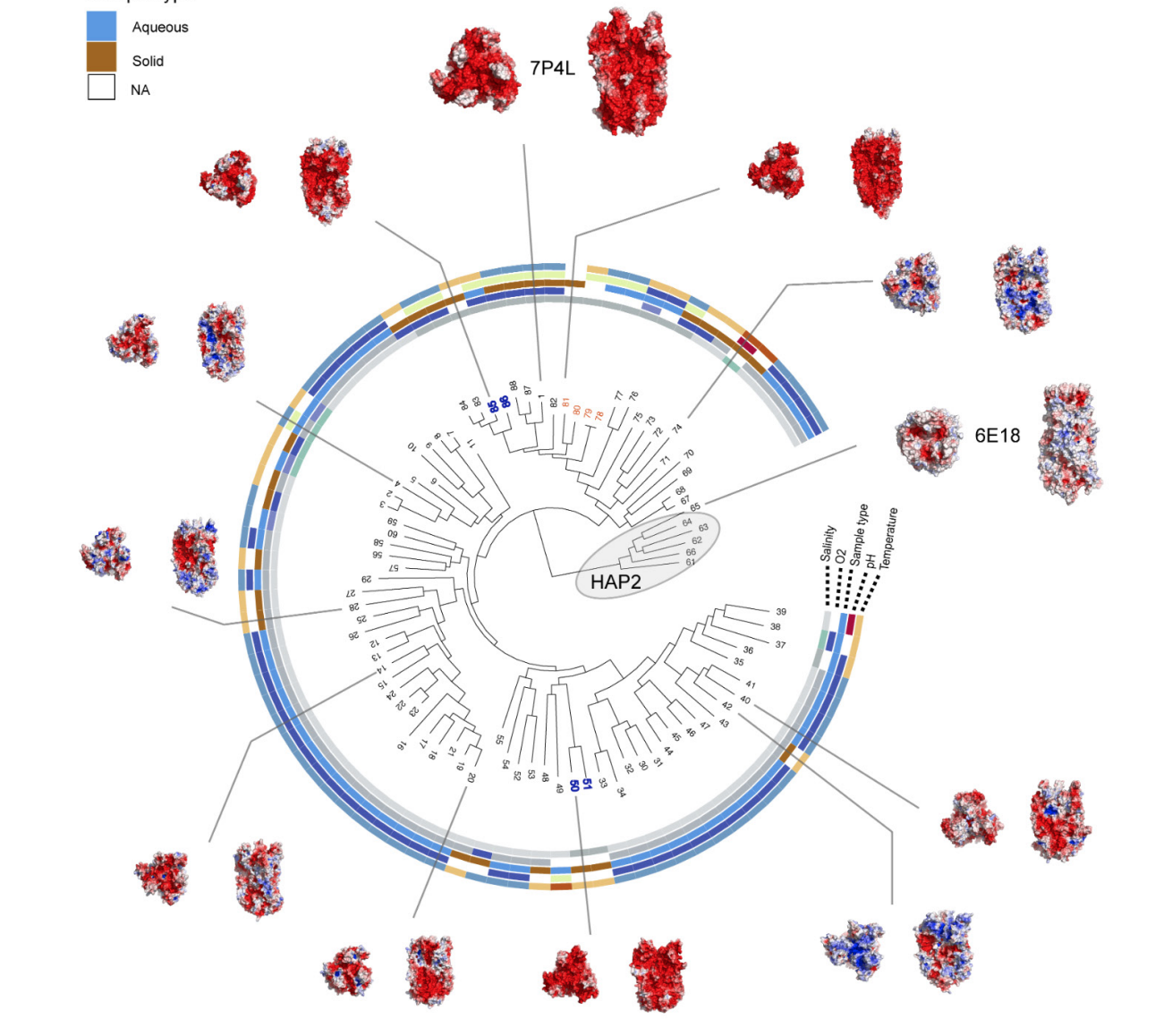 | Moi D., Nishio S., Li X., Valansi C., Langleib M., Brukman N.G., Flyak K., Dessimoz C., de Sanctis D., Tunyasuvunakool K., Jumper J., Grana M., Romero H., Aguilar P.S., Jovine L., Podbilewicz B. (2022) "Discovery of archaeal fusexins homologous to eukaryotic HAP2/GCS1 gamete fusion proteins" Nat Commun 13, 3880 (2022). | Link |
 | Nakajima K.P., Valansi C., Kurihara D., Sasaki N., Podbilewicz B. & Higashiyama T. (2022) "Live imaging-based assay for visualising species-specific interactions in gamete adhesion molecules" Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 10;12(1):9609. | |
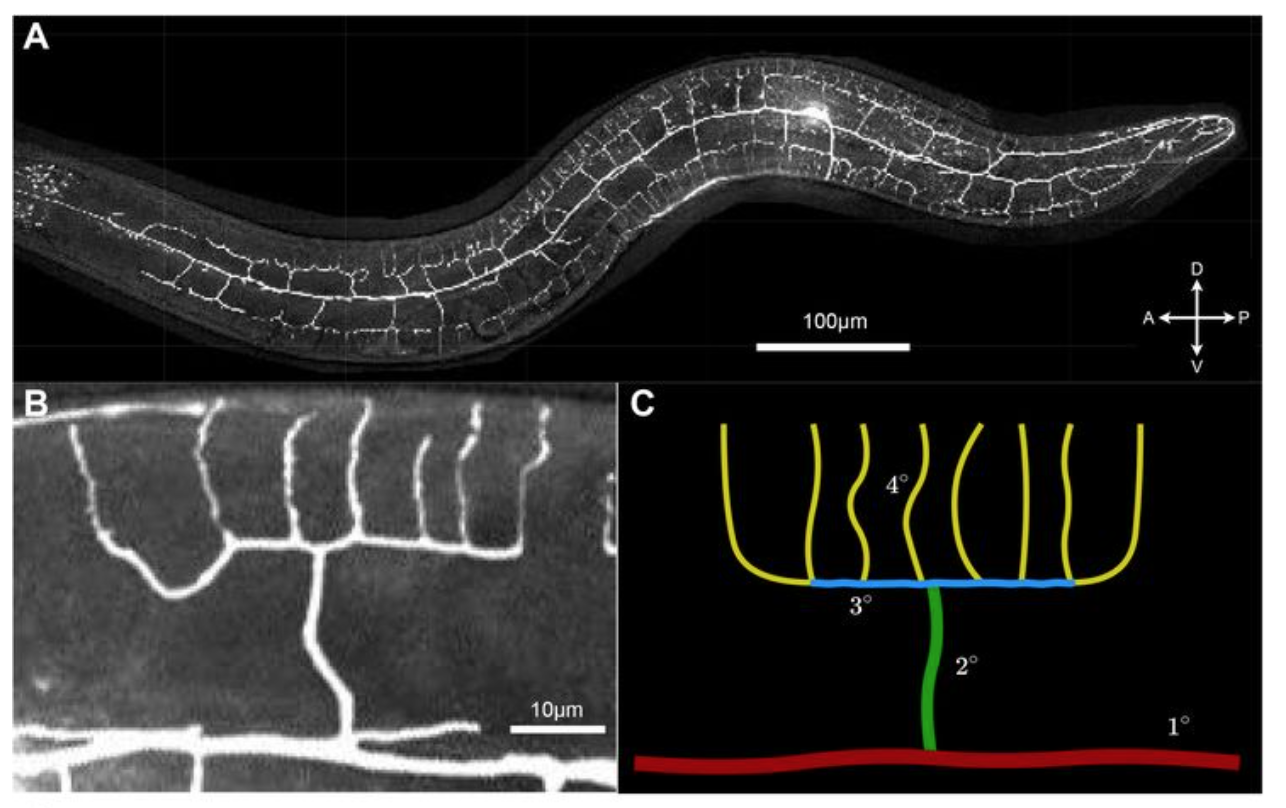 | Yuval O., Iosilevskii Y., Meledin A., Podbilewicz B., Shemesh T. (2021) "Neuron tracing and quantitative analyses of dendritic architecture reveal symmetrical three-way-junctions and phenotypes of git-1 in C. elegans" PLoS Comput Biol 17(7): e1009185. | Link |
 | Meledin A., Li X., Matveev E., Gildor B., Katzir O. & Podbilewicz B. (2020). "EFF-1 promotes muscle fusion, paralysis and retargets infection by AFF-1-coated viruses in C. elegans". bioRxiv (Preprint). | Link |
 | Kravtsov, V., Oren-Suissa, M., & Podbilewicz, B. (2017). "AFF-1 fusogen can rejuvenate the regenerative potential of adult dendritic trees via self-fusion". Development, dev-150037. | |
 | Valansi, C., D. Moi, E. Leikina, E. Matveev, M. Graña, L. V. Chernomordik, H. Romero, P. S. Aguilar and B. Podbilewicz (2017). "Arabidopsis HAP2/GCS1 is a gamete fusion protein homologous to somatic and viral fusogens." The Journal of Cell Biology. | |
 | Oren-Suissa, M., Gattegno, T., Kravtsov, V., Podbilewicz, B. (2017).Extrinsic Repair of Injured Dendrites as a Paradigm for Regeneration by Fusion in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics Early online March 10, 2017; DOI: 10.1534/genetics.116.196386 | |
 | Smurova, K. and Podbilewicz, B. (2016) RAB-5-and DYNAMIN-1-Mediated Endocytosis of EFF-1 Fusogen Controls Cell-Cell Fusion. Cell reports, 14(6), pp.1517-1527. | |
 | Greenblum, A., Sznitman, R., Fua, P., Arratia, P.E., Oren, M., Podbilewicz, B., and Sznitman, J. (2014). Dendritic tree extraction from noisy maximum intensity projection images in C. elegans. Biomedical engineering online 13, 74. | |
 | Perez-Vargas, J., Krey, T., Valansi, C., Avinoam, O., Haouz, A., Jamin, M., Raveh-Barak, H., Podbilewicz, B., and Rey, F.A. (2014). Structural basis of eukaryotic cell-cell fusion. Cell 157, 407-419. | |
 | Yaniv, S.P., Issman-Zecharya, N., Oren-Suissa, M., Podbilewicz, B., and Schuldiner, O. (2012). Axon regrowth during development and regeneration following injury share molecular mechanisms. Current biology : CB 22, 1774-1782. | |
 | Avinoam, O., Fridman, K., Valansi, C., Abutbul, I., Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, T., Maurer, U.E., Sapir, A., Danino, D., Grunewald, K., White, J.M., et al. (2011). Conserved eukaryotic fusogens can fuse viral envelopes to cells. Science 332, 589-592 | |
 | Oren-Suissa, M., Hall, D.H., Treinin, M., Shemer, G., and Podbilewicz, B. (2010). The fusogen EFF-1 controls sculpting of mechanosensory dendrites. Science 328, 1285-1288. | |
 | Chen, A., Leikina, E., Melikov, K., Podbilewicz, B., Kozlov, M.M., and Chernomordik, L.V. (2008). Fusion-pore expansion during syncytium formation is restricted by an actin network. Journal of cell science 121, 3619-3628. | |
 | Kolotuev, I., and Podbilewicz, B. (2008). Changing of the cell division axes drives vulva evolution in nematodes. Developmental biology 313, 142-154. | |
 | Kiontke, K., Barriere, A., Kolotuev, I., Podbilewicz, B., Sommer, R., Fitch, D.H., and Felix, M.A. (2007). Trends, stasis, and drift in the evolution of nematode vulva development. Current biology : CB 17, 1925-1937. | |
 | Margalit, A., Neufeld, E., Feinstein, N., Wilson, K.L., Podbilewicz, B., and Gruenbaum, Y. (2007). Barrier to autointegration factor blocks premature cell fusion and maintains adult muscle integrity in C. elegans. The Journal of cell biology 178, 661-673. | |
 | Sapir, A., Choi, J., Leikina, E., Avinoam, O., Valansi, C., Chernomordik, L.V., Newman, A.P., and Podbilewicz, B. (2007). AFF-1, a FOS-1-regulated fusogen, mediates fusion of the anchor cell in C. elegans. Developmental cell 12, 683-698. | |
 | Gattegno, T., Mittal, A., Valansi, C., Nguyen, K.C., Hall, D.H., Chernomordik, L.V., and Podbilewicz, B. (2007). Genetic control of fusion pore expansion in the epidermis of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular biology of the cell 18, 1153-1166. | |
 | Podbilewicz, B., Leikina, E., Sapir, A., Valansi, C., Suissa, M., Shemer, G., and Chernomordik, L.V. (2006). The C. elegans developmental fusogen EFF-1 mediates homotypic fusion in heterologous cells and in vivo. Developmental cell 11, 471-481. | |
 | Cassata, G., Shemer, G., Morandi, P., Donhauser, R., Podbilewicz, B., and Baumeister, R. (2005). ceh-16/engrailed patterns the embryonic epidermis of Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 132, 739-749. | |
 | Shemer, G., Suissa, M., Kolotuev, I., Nguyen, K.C., Hall, D.H., and Podbilewicz, B. (2004). EFF-1 is sufficient to initiate and execute tissue-specific cell fusion in C. elegans. Current biology : CB 14, 1587-1591. | |
 | Broday, L., Kolotuev, I., Didier, C., Bhoumik, A., Gupta, B.P., Sternberg, P.W., Podbilewicz, B., and Ronai, Z. (2004a). The small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) is required for gonadal and uterine-vulval morphogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes & development 18, 2380-2391. | |
 | Broday, L., Kolotuev, I., Didier, C., Bhoumik, A., Podbilewicz, B., and Ronai, Z. (2004b). The LIM domain protein UNC-95 is required for the assembly of muscle attachment structures and is regulated by the RING finger protein RNF-5 in C. elegans. The Journal of cell biology 165, 857-867. | |
 | Kolotuev, I., and Podbilewicz, B. (2004). Pristionchus pacificus vulva formation: polarized division, cell migration, cell fusion, and evolution of invagination. Developmental biology 266, 322-333. | |
 | Louvet-Vallee, S., Kolotuev, I., Podbilewicz, B., and Felix, M.A. (2003). Control of vulval competence and centering in the nematode Oscheius sp. 1 CEW1. Genetics 163, 133-146 | |
 | Shemer, G., and Podbilewicz, B. (2002). LIN-39/Hox triggers cell division and represses EFF-1/fusogen-dependent vulval cell fusion. Genes & development 16, 3136-3141. | |
 | Mohler, W.A., Shemer, G., del Campo, J.J., Valansi, C., Opoku-Serebuoh, E., Scranton, V., Assaf, N., White, J.G., and Podbilewicz, B. (2002). The type I membrane protein EFF-1 is essential for developmental cell fusion. Developmental cell 2, 355-362. | |
 | Rabin, Y., and Podbilewicz, B. (2000). Temperature-controlled microscopy for imaging living cells: apparatus, thermal analysis and temperature dependency of embryonic elongation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Journal of microscopy 199, 214-223. | |
 | Shemer, G., Kishore, R., and Podbilewicz, B. (2000). Ring formation drives invagination of the vulva in Caenorhabditis elegans: Ras, cell fusion, and cell migration determine structural fates. Developmental biology 221, 233-248. | |
 | Sharma-Kishore, R., White, J.G., Southgate, E., and Podbilewicz, B. (1999). Formation of the vulva in Caenorhabditis elegans: a paradigm for organogenesis. Development 126, 691-699. | |
 | Podbilewicz, B. (1996). ADM-1, a protein with metalloprotease- and disintegrin-like domains, is expressed in syncytial organs, sperm, and sheath cells of sensory organs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular biology of the cell 7, 1877-1893. | |
 | Podbilewicz, B., and White, J.G. (1994). Cell fusions in the developing epithelial of C. elegans. Developmental biology 161, 408-424. |