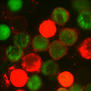
 | Chen, A., Leikina, E., Melikov, K., Podbilewicz, B., Kozlov, M.M., and Chernomordik, L.V. (2008). Fusion-pore expansion during syncytium formation is restricted by an actin network. Journal of cell science 121, 3619-3628. | PDF |
 | Kolotuev, I., and Podbilewicz, B. (2008). Changing of the cell division axes drives vulva evolution in nematodes. Developmental biology 313, 142-154. | PDF |
 | Kiontke, K., Barriere, A., Kolotuev, I., Podbilewicz, B., Sommer, R., Fitch, D.H., and Felix, M.A. (2007). Trends, stasis, and drift in the evolution of nematode vulva development. Current biology : CB 17, 1925-1937. | PDF |
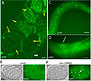 | Margalit, A., Neufeld, E., Feinstein, N., Wilson, K.L., Podbilewicz, B., and Gruenbaum, Y. (2007). Barrier to autointegration factor blocks premature cell fusion and maintains adult muscle integrity in C. elegans. The Journal of cell biology 178, 661-673. | PDF |
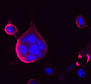 | Sapir, A., Choi, J., Leikina, E., Avinoam, O., Valansi, C., Chernomordik, L.V., Newman, A.P., and Podbilewicz, B. (2007). AFF-1, a FOS-1-regulated fusogen, mediates fusion of the anchor cell in C. elegans. Developmental cell 12, 683-698. | PDF |
 | Gattegno, T., Mittal, A., Valansi, C., Nguyen, K.C., Hall, D.H., Chernomordik, L.V., and Podbilewicz, B. (2007). Genetic control of fusion pore expansion in the epidermis of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular biology of the cell 18, 1153-1166. | PDF |
 | Podbilewicz, B., Leikina, E., Sapir, A., Valansi, C., Suissa, M., Shemer, G., and Chernomordik, L.V. (2006). The C. elegans developmental fusogen EFF-1 mediates homotypic fusion in heterologous cells and in vivo. Developmental cell 11, 471-481. | PDF |
 | Cassata, G., Shemer, G., Morandi, P., Donhauser, R., Podbilewicz, B., and Baumeister, R. (2005). ceh-16/engrailed patterns the embryonic epidermis of Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 132, 739-749. | PDF |
 | Shemer, G., Suissa, M., Kolotuev, I., Nguyen, K.C., Hall, D.H., and Podbilewicz, B. (2004). EFF-1 is sufficient to initiate and execute tissue-specific cell fusion in C. elegans. Current biology : CB 14, 1587-1591. | PDF |
 | Broday, L., Kolotuev, I., Didier, C., Bhoumik, A., Gupta, B.P., Sternberg, P.W., Podbilewicz, B., and Ronai, Z. (2004a). The small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) is required for gonadal and uterine-vulval morphogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes & development 18, 2380-2391. | PDF |
 | Broday, L., Kolotuev, I., Didier, C., Bhoumik, A., Podbilewicz, B., and Ronai, Z. (2004b). The LIM domain protein UNC-95 is required for the assembly of muscle attachment structures and is regulated by the RING finger protein RNF-5 in C. elegans. The Journal of cell biology 165, 857-867. | PDF |
 | Kolotuev, I., and Podbilewicz, B. (2004). Pristionchus pacificus vulva formation: polarized division, cell migration, cell fusion, and evolution of invagination. Developmental biology 266, 322-333. | PDF |











